The ForMAX beamline is equipped with two horizontally deflecting monochromators: either a “high-resolution” double crystal monochromator (FMB Oxford) or a “high-flux” double multilayer monochromator (Axilon). The former is the standard monochromator for SWAXS and the latter for full-field imaging. The beam passes onto dynamically bendable mirrors in Kirkpatrick-Baez geometry (IRELEC), providing harmonic rejection and the possibility for independent focusing/collimation in vertical and horizontal directions. Secondary optics in the experimental station will provide the possibility of further decreasing the beam size to ≈ 10 μm or increasing to ≈ 5 mm (not yet in operation).
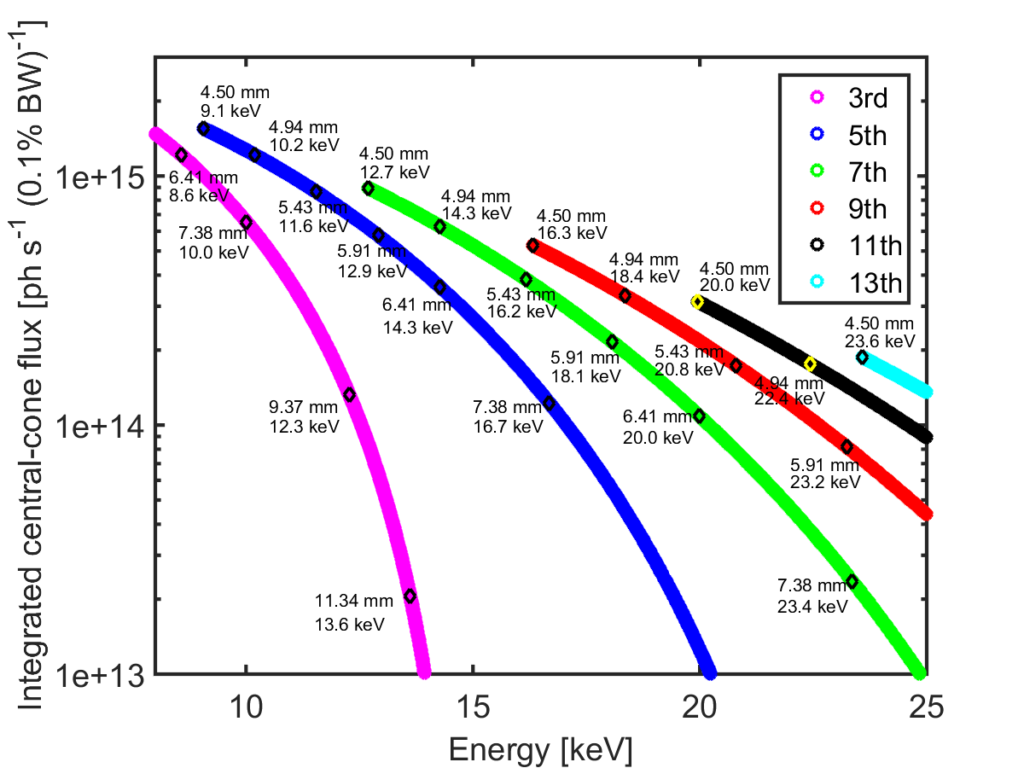
For the approximate flux emitted from the undulator, see figure below:
For details on the optics, see either the ‘beamline’ paper or the table below:
Publication
| X-ray source | In-vacuum undulator (IVU), 3 m magnetic length, 17 mm period, 166 periods, 4.5 mm minimal magnetic gap. |
| Energy range | 8-25 keV, using 3rd-13th harmonics of the IVU. |
| Crystal monochromator (hDCM) | Cryo-cooled horizontally deflecting double-bounce Si(111) crystal monochromator with fixed exit. Positioned 27 m downstream of the source. |
| Multilayer monochromator (hDMM) | Water-cooled horizontally deflecting double-bounce multilayer monochromator with fixed exit. W/B4C and Ru/B4C coatings. Positioned at 25 m. |
| Focusing mirrors | Vertically (VFM; 30.2 m from source) and horizontally (HFM;31 m from source) bouncing mirrors in Kirkpatrick-Baez geometry. Dynamically bendable flat mirrors, allowing focusing the beam at various planes down to sample position, collimating the beam, or no focusing, independently in vertical and horizontal directions (bending radii 5-100 km). Si, Rh, and Pt stripes for harmonic rejection. |
| Sample position | 42 m downstream of the source. |
| Flux at sample position | >1013 ph/s using the hDCM, >1014 ph/s using the hDMM. |
| Beam size at sample position (FWHM; vertical x horizontal) | Variable between 1x1 mm2 and 15x60 µm 2. Larger (approximately 5x5 mm2; not yet commissioned) and smaller (10x10 µm 2 at 16.3 keV) beam sizes are possible using secondary optics in the experimental station. |